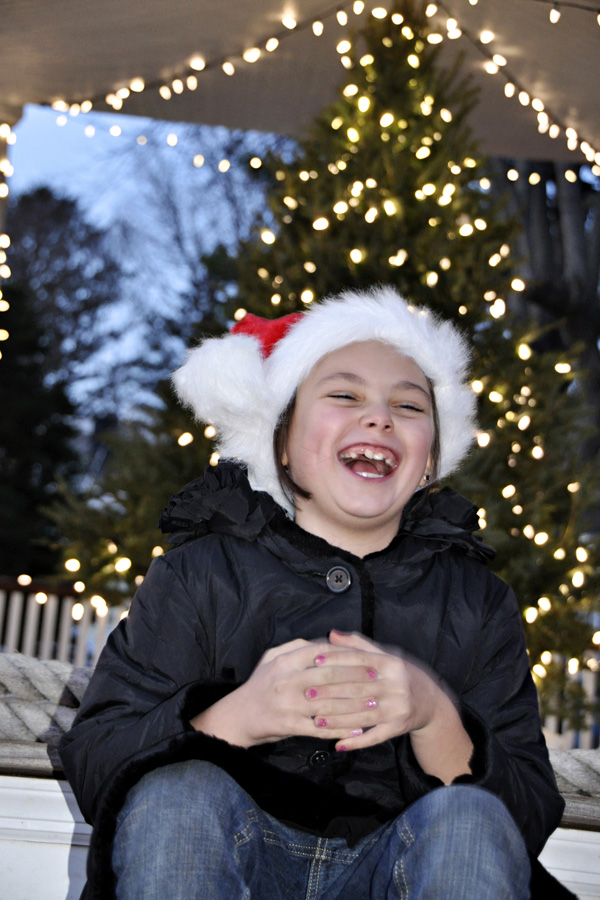
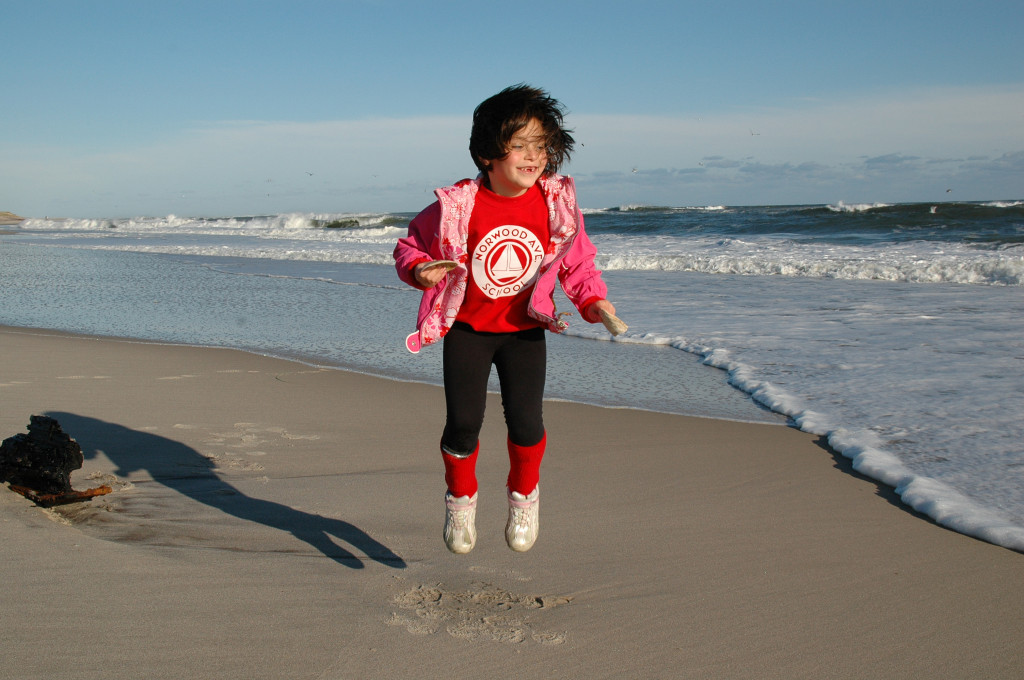
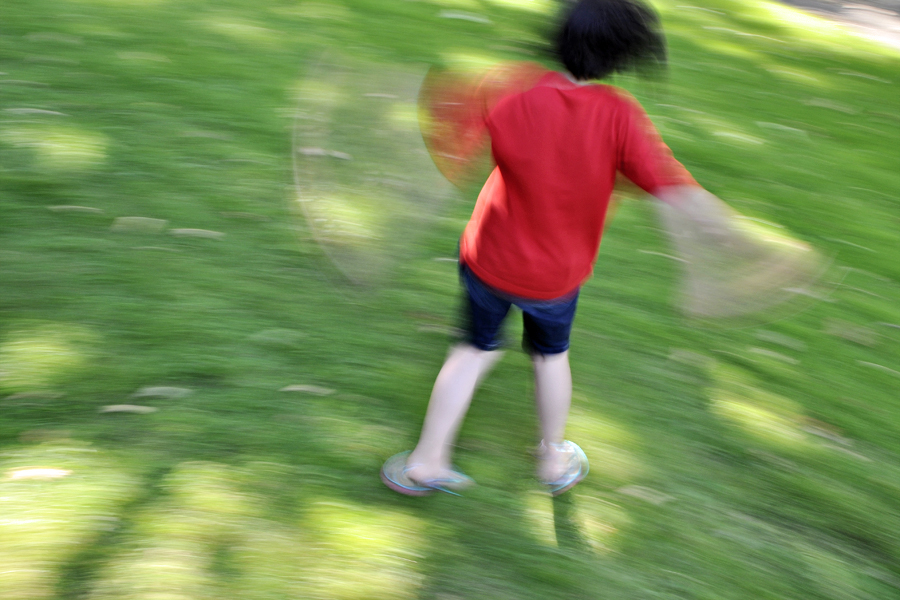
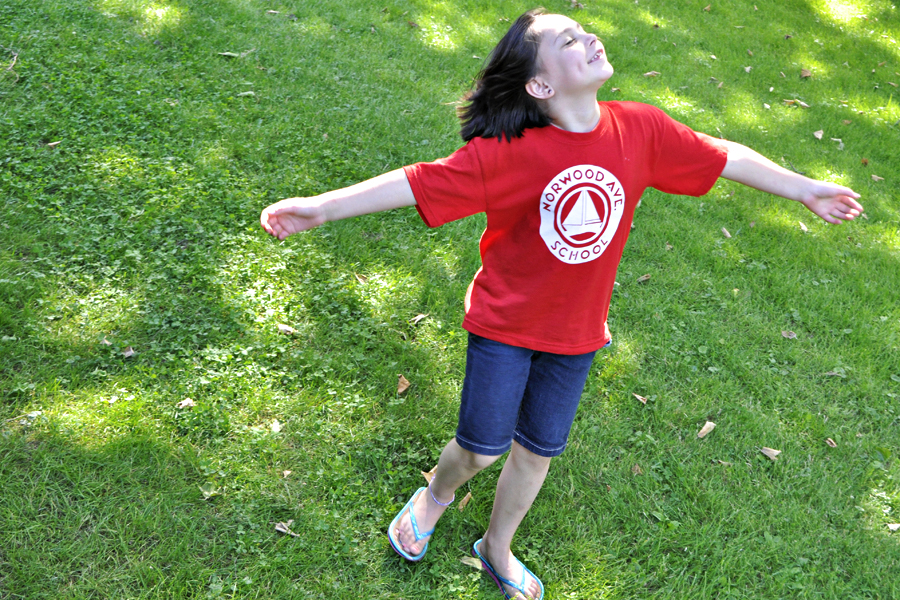
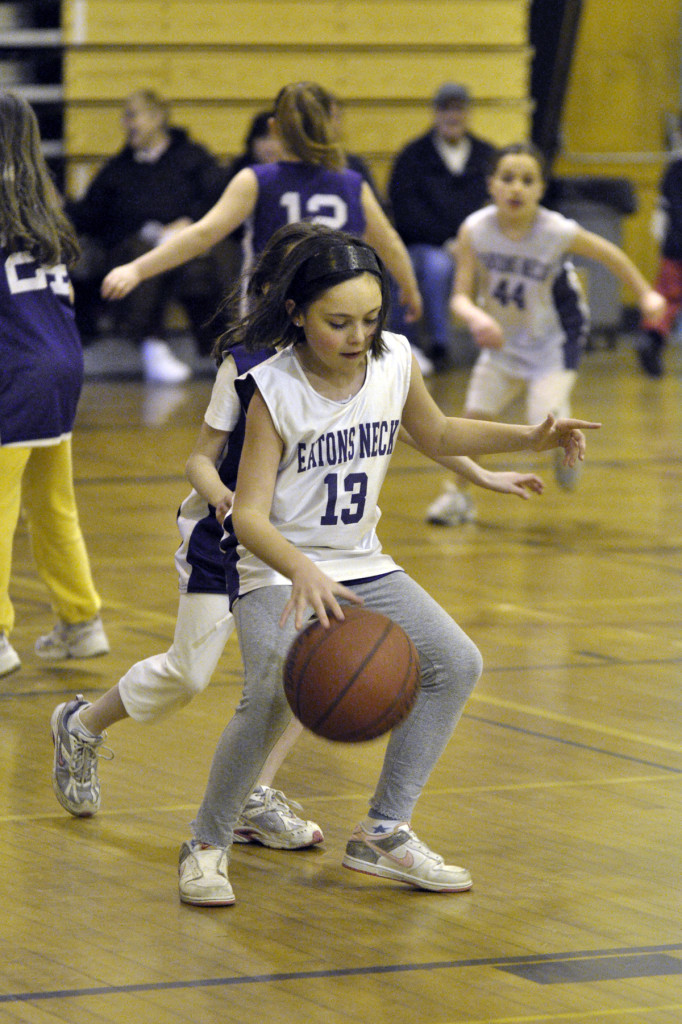So while talking with friends who are all new DSLR owners this past weekend, we discussed the solutions for the most common problems people have with their photos. So of course, it sparked an idea for a blog post. Here is part 1: “My Photos Are Blurry.”
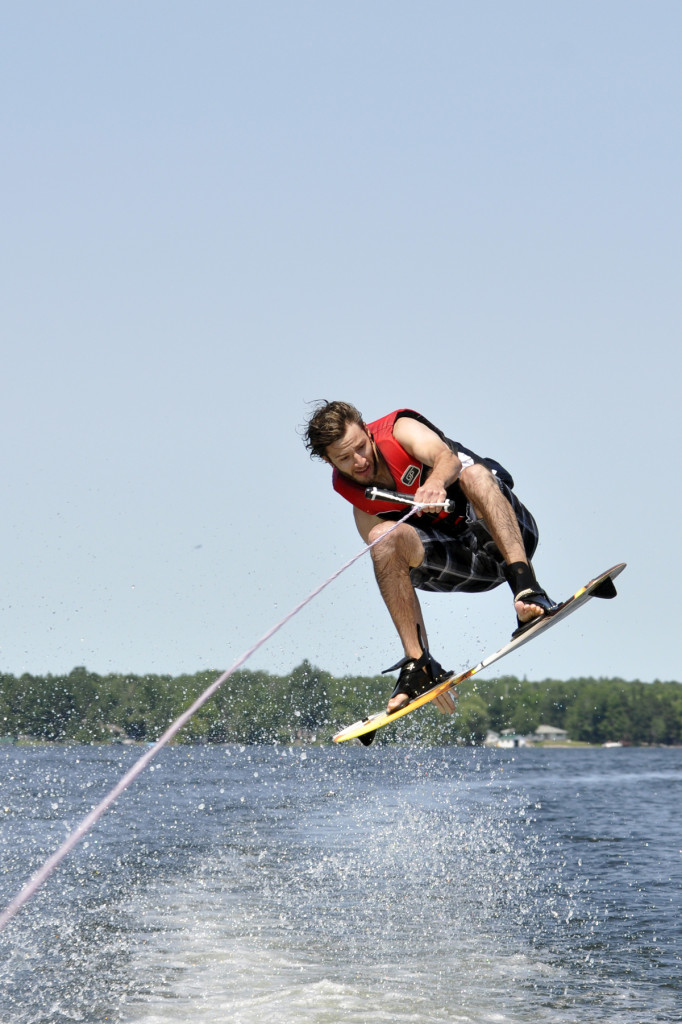
The reason for a blurry photo is that the shutter speed is too slow to stop either fast moving action or camera shake in low light situations. The faster action moves, the faster the shutter speed required to stop the action; the longer your lens setting (telephoto), the faster the shutter speed required to stop camera shake since the shake is magnified (think about looking through powerful binoculars and how hard it is to hold them without the seeing shake); and finally, in lower the lighting conditions, the shutter speed slows down to let in more light, making it harder to hand hold.
So what to do? First, you need to understand what the ideal shutter speed is for hand-holding to avoid camera shake. The quick answer to to shoot at a shutter sped that is no slower than the reciprocal of the focal length setting of your lens. So if you are zoomed out to 300mm to catch sports, nature, wildlife or candid portraits, the ideal shutter sped will be 1/300th of a second or faster to stop hand shake blur. However, with today’s stabilized lenses, you can shoot a 2-3 or even 4 stops slower with no resulting hand-shake. Second, understand that it is almost impossible for anyone to hand hold the camera at any focal length setting if the shutter speed goes below 1/30th of a second. Thirdly, if action is moving fast, like soccer or basketball, you will need a shutter speed of approx. 1/500th of a second. If the action moves even faster than that, such as car racing or horse racing, you will need to shoot even faster (1/1000th, 1/2500th, etc.(.
Solution 1: Open your aperture to let in more light and the camera will pick a faster shutter speed.
If you set your camera to aperture priority, move the aperture towards a wider opening (e.g., F/6.3, F/5.6, F/3.5) and watch your shutter speed get faster. Hopefully, you will be able to get a shutter speed / aperture combination that allows you to have a fast shutter speed for the action or zoom setting. Be mindful that with an open aperture, you have less depth of field, so precisely focusing on the critical part of your image is very important.
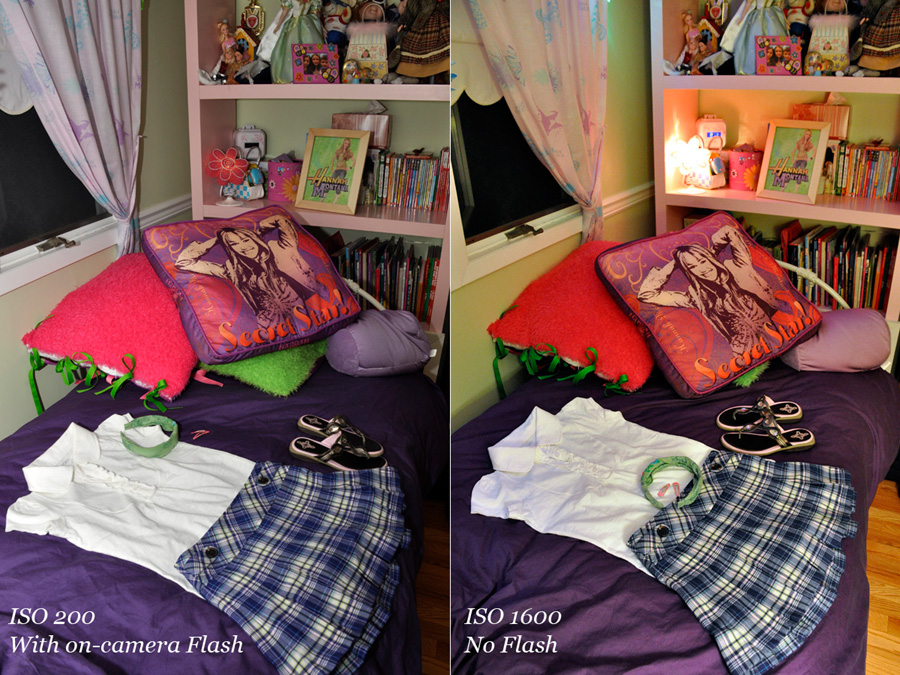
Solution 2: If opening the aperture does not give you a shutter speed high enough to action blur or stop hand shake from slow shutter speeds as a result of low light or long telephoto settings, then the next solution is to boost your ISO higher. A higher ISO, will automatically provide you with higher shutter speeds. While your photo might have a little more noise or not as vibrant of color, you will be able to shoot the image. (Some DSLRs have really great high ISO capabilities, so don’t be afraid to try higher ISO settings).
Solution 3 (and my least favorite): If neither solution above works, then you can try to increase the lighting in the scene. One way is by adding flash. Flash will certainly freeze action and eliminate hand shake blur (as long as you are not in night time portrait mode). While flash can lead to an artificial feeling in your shot, hence my reason for it not being my favorite, it can do the job effectively and send you home with images of the moment. Remember, however, that flash can only cover a certain distance, and is sometimes not allowed at certain venues, so solutions 1 or 2 or a combination of both may be your only choices to correct the problem.
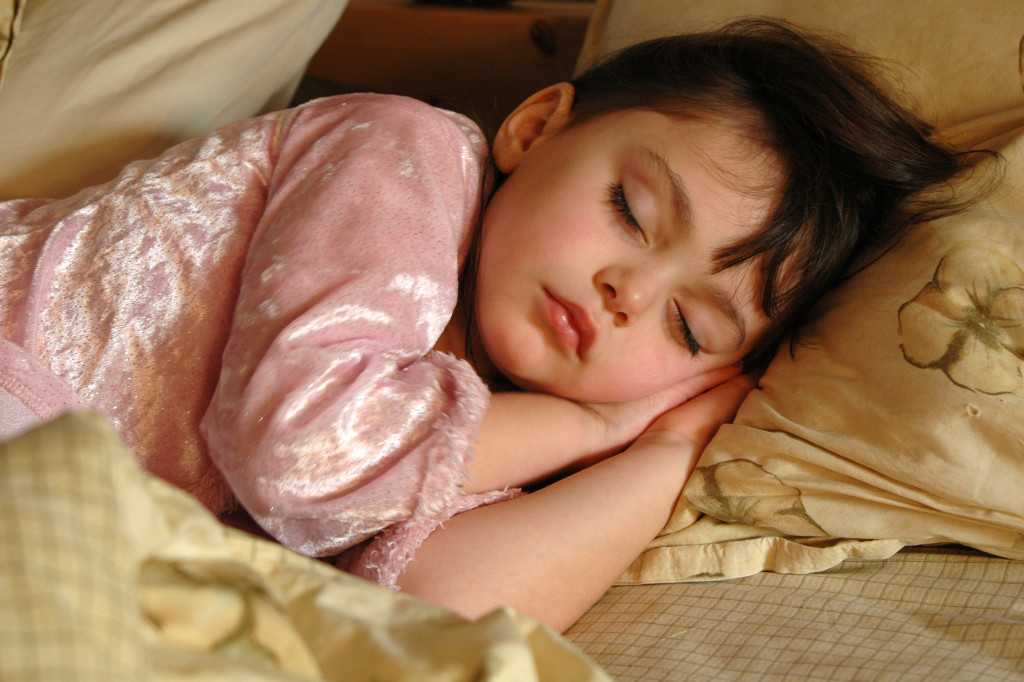
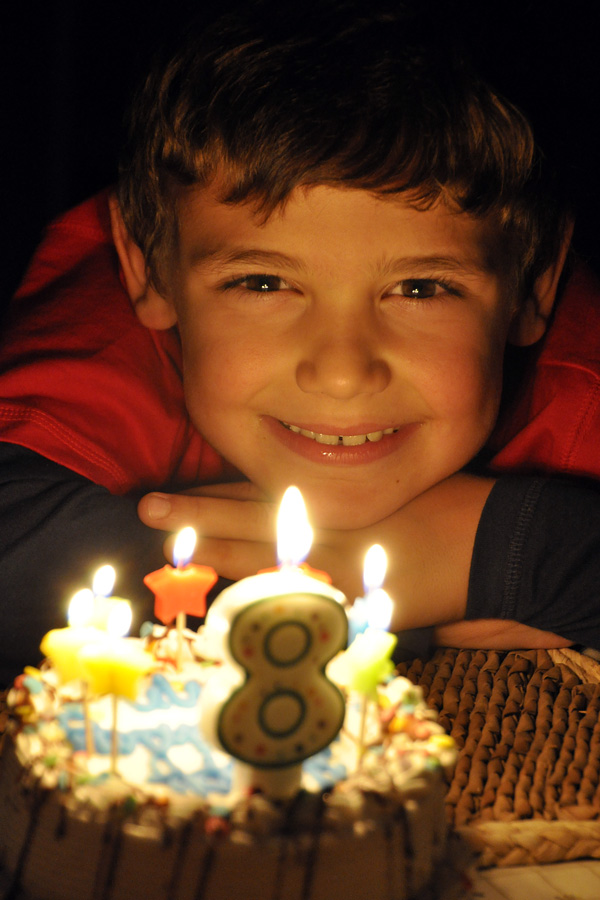
The image above would have been completely different had I used flash. So I boosted my ISO to 1600 so that the little bit of light coming into the room could be captured naturally. My lens was zoomed to 60mm, making the magic shutter speed 1/60th of a second. However, with my stabilized lens, I was fortunate to be able to catch the image at 1/8th of a second, the fastest shutter speed I could achieve with the given lighting, ISO setting and open aperture (F/4). The VC stabilization allowed me to shoot 3 stops slower than what would be normally required.
And of course, a solution that works the best for low light situations is a tripod. As long as there is no movement in your shot, a tripod will stabilize your camera and let you shoot at rather slow shutter speeds. Tripods are the most essential tool for landscape and nature photographers since a smaller aperture like F/11, F/16 or F/22 are required to achieve deep depth of field, but shutter speeds are naturally slower.
Next time you are shooting in low light, shooting at a longer telephoto zoom setting, or shooting action, consider the solutions above and you should find your images will be sharp as a result.