Water is a compelling photographic subject. And how you capture it makes an impression on the viewer. Freezing the action for crystal clear water droplets from a crashing wave or pool splashes conveys power and energy. Slowing the motion down to create a milky white stream of water creates a more serene picture.
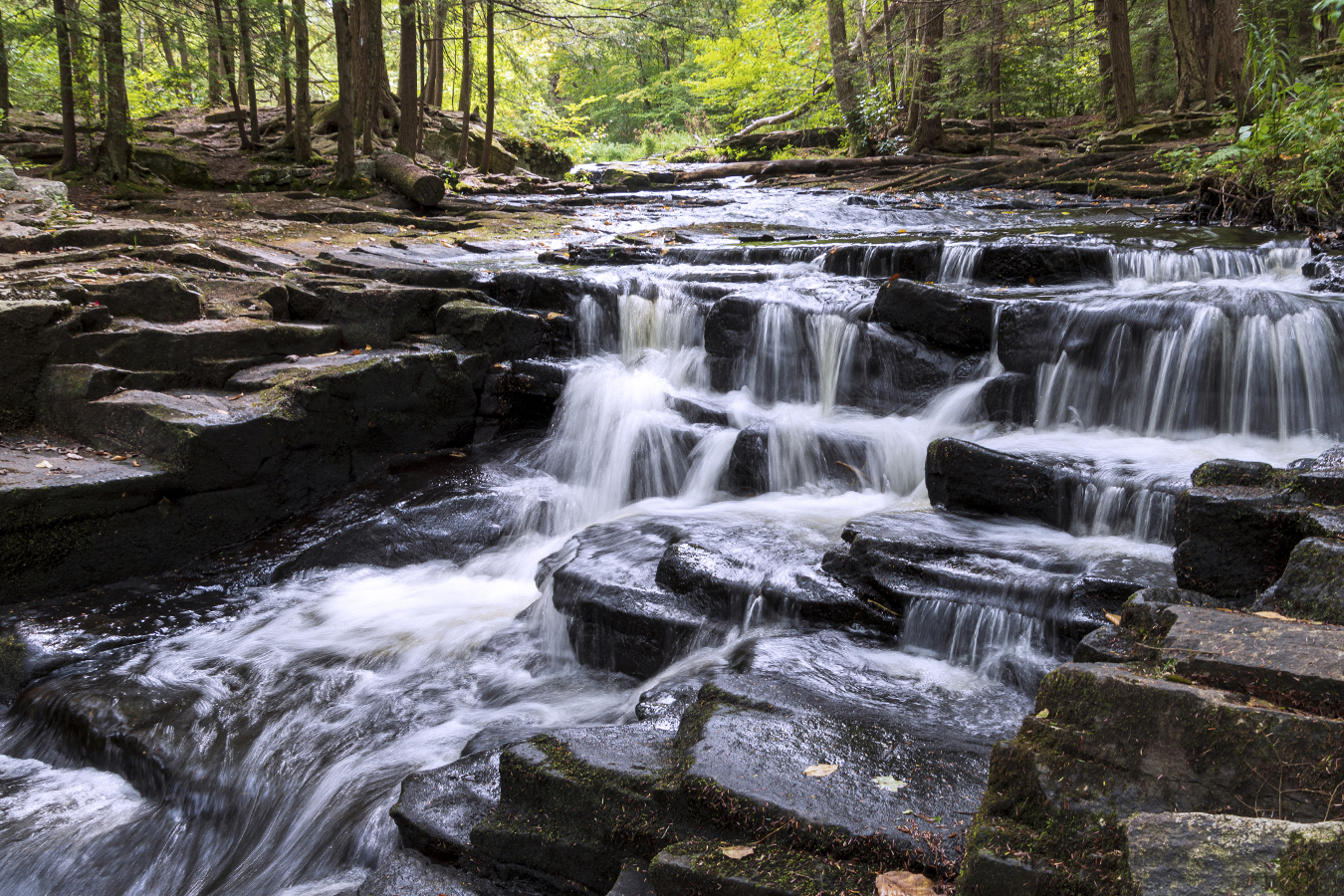 In this photo taken on the Little Falls Trail in Promised Land State Park, Poconos, PA, I hiked in mid-morning with my 18-400mm all-in-one lens as well as an electronics cable release designed for your camera and my travel tripod, two must-have accessories to create silky water fall action. Getting as close down and into the flowing water as possible creates a more dramatic perspective.
In this photo taken on the Little Falls Trail in Promised Land State Park, Poconos, PA, I hiked in mid-morning with my 18-400mm all-in-one lens as well as an electronics cable release designed for your camera and my travel tripod, two must-have accessories to create silky water fall action. Getting as close down and into the flowing water as possible creates a more dramatic perspective.
Settings are very important. First, set your camera to aperture priority and choose an aperture that will give you deep depth of field (between F11-F22 is ideal) so that your foreground to background will be in focus. I used F11 here. Next, select ISO 100. Now look thru the viewfinder and see if your shutter speed is below 1/15th second (I shot my image above at 1/6th second). You can change your aperture to make the shutter speed faster or slower. If you move the aperture from F11 to F16, the shutter speed be slower. If you open up your aperture to F8 to let light more light in, the shutter speed will be faster. Start shooting to see your effect and change your aperture until the image looks the way you want it to.
Since you will be shooting at slow shutter speeds below 1/60th second, you will not be able to handhold the camera. You must use a sturdy tripod and a cable release to ensure there is no camera shake.
The three settings involved in creating an image of a waterfall are referred to as the exposure triangle. The ISO, the aperture and the shutter speed all work in concert to create the effect. So your constant will be your ISO. The second that you will work with is your aperture. Opening or closing the aperture will change the shutter speed to be faster or slower. The shutter speed is ultimately the setting that will either freeze the water (faster shutter speed) or create the silky effect (slower shutter speed).
And the last tip for any landscape photo is to focus about a third of the way into the scene. This will give you the best results for foreground to background focus.
This tip is a good self-assignment for any season. So, find a park with waterfalls within driving distance and head out with your wide-angle lens, tripod and cable release.